Envision.
Build.
Sustain.
Planning for an Integrated, Resilient Future

Yolo Bypass Cache Slough Partnership
A Vision for a New Era
CA Senate Bill 369 directed Partnership agencies to work in collaboration to advance the following objectives:
- Prioritize projects that accommodate multiple objectives in the YBCS region.
- Identify project implementation challenges and work collaboratively to resolve those challenges.
- Develop programmatic and expedited approaches for regulatory compliance. Identify funding mechanisms for project implementation and long-term operations and maintenance.
- Develop strategies to foster regional agricultural sustainability, recreational opportunities, and long-term water supply reliability.
Yolo Bypass Cache Slough Partnership
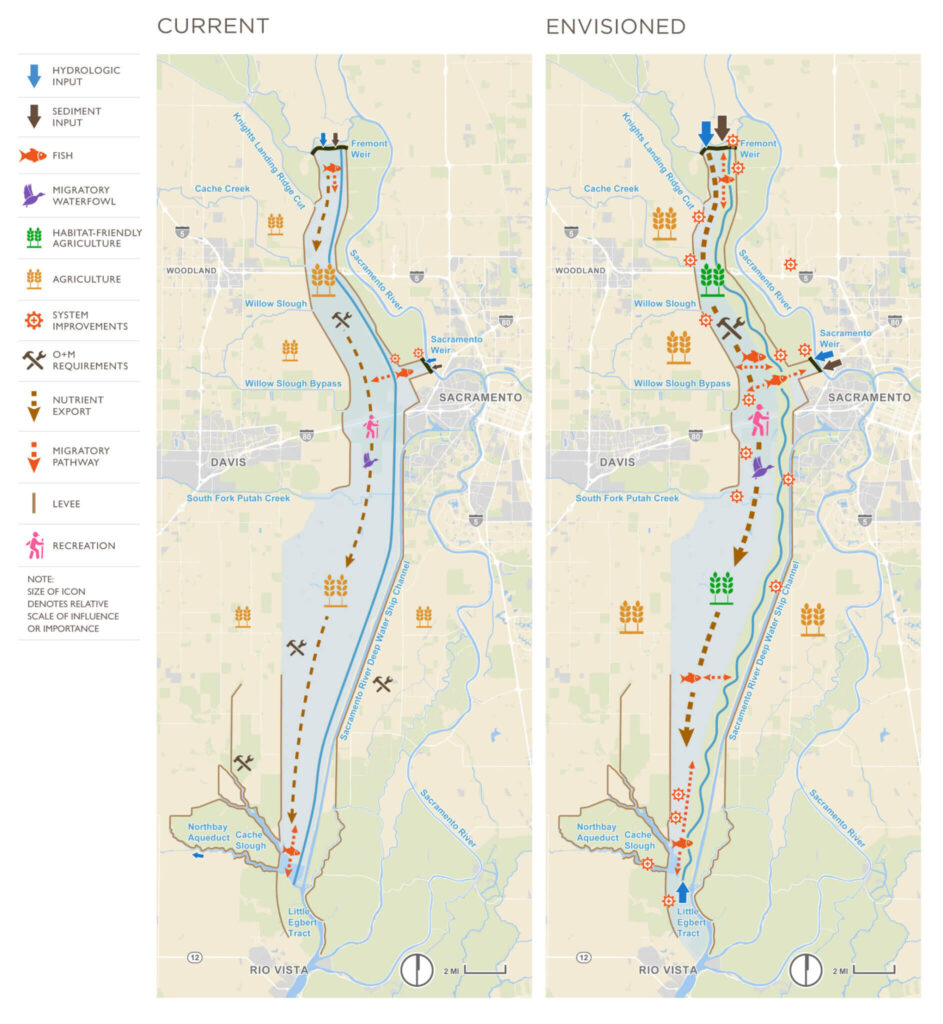
The Yolo Bypass Cache Slough Partnership is a dynamic and results-focused response to those challenges. Local, state, and federal agency members of the Partnership – working closely with regional agencies, interested parties, and Native American Tribes – are jointly planning and implementing projects capable of delivering multiple benefits across a shared YBCS landscape. Flood risk management, fisheries and wildlife habitat, water supply, water quality, agriculture, and recreation – collectively referred to as the Partnership Pillars – are all central to collaborative planning for a vibrant future for the region’s residents, businesses, and ecosystem. Further, the Partnership is committed to making diversity, equity, and inclusion central to its efforts to accrue benefits across these pillars.
Yolo Bypass Cache Slough Region
The Yolo Bypass is a 40-mile long, 59,000 acre federal flood management facility, built in the 1930s to protect lives and property across the Sacramento metropolitan area.
The Cache Slough is located primarily within the County of Solano, intersecting with the southern portion of the Yolo Bypass. Cache Slough supports remnant tidal habitat where restoration of natural conditions could benefit delta smelt and other native aquatic species. Cache Slough is also a regionally significant agricultural area where the location of multiple-benefit projects could affect the operations and maintenance practices of agricultural diverters and core flood control and levee maintenance responsibilities of reclamation districts within the Cache Slough Complex.
Together, the Yolo Bypass and Cache Slough region presents unparalleled opportunities for multiple-benefit projects that improve flood protection, fisheries and wildlife habitat, water supply and water quality, agriculture, and recreational opportunities. As such, the Yolo Bypass and Cache Slough region is the focus of an increasing number of federal, state, and locally developed projects intended to improve these multiple public values.
Today, the Yolo Bypass Cache Slough region (YBCS) is a microcosm of challenges and opportunities facing water managers and planners around California. Climate change is increasing the frequency and intensity of floods and droughts in the YBCS, adversely impacting the region.

Vision
The local, state, and federal agency members of the Partnership – working closely with other agencies, interested parties, and Native American Tribes – are jointly planning and implementing projects capable of delivering multiple benefits across a shared YBCS landscape.
Partnership Goals
In recognition of the advantages of an integrated approach, a new era of multi-benefit collaborative planning began in 2016 when representatives of 15 agencies executed the Yolo Bypass Cache Slough Partnership Memorandum of Understanding. Since 2016, the Partner agencies have been developing a Program that encourages collaboration on regional solutions to implement landscape-level change.
The success of the Partnership will require proactive investment, leveraging of resources, and sustainable funding mechanisms for Partnership activities and long-term management of the YBCS system and its features.
Flood
Agriculture
Habitat
Water Supply
Recreation
Water Quality
Understanding the Importance of the YBCS Region
Centered between the Sacramento and American Rivers and the Sacramento-San Joaquin Delta, the YBCS is the heart of a vast watershed – and central to a robust regional agricultural economy, reliable water supply, and resilient ecosystem, in addition to flood risk reduction.
Partners
In recognition of the advantages of an integrated approach, a new era of multi-benefit collaborative planning began when local, state and federal agency representatives executed the YBCS Memorandum of Understanding. In September 2021, SB 369 added the West Sacramento Area Flood Control Agency.
